Panda Temple project is a natural gas fired combined-cycle power plant located in the city of Temple, Texas, US.
The Temple power plant will spread across 250 acres in the Synergy Industrial Park. The engineering and design work of the plant began in February 2012. Construction work was started in July 2012 and commercial operation of the power plant began in September 2014.
A consortium of Siemens and Bechtel constructed the power plant under a $300m turnkey contract. The power generated by the plant fulfils the power needs of approximately 750,000 homes in central and north Texas.
The plant is expected to benefit the state’s future energy requirements and generate approximately $1.6bn in state revenue during construction as well as the first ten years of operation.
The project employed between 400 and 500 workers during construction.
Turbines, equipment and Flex-Plant-30 technology
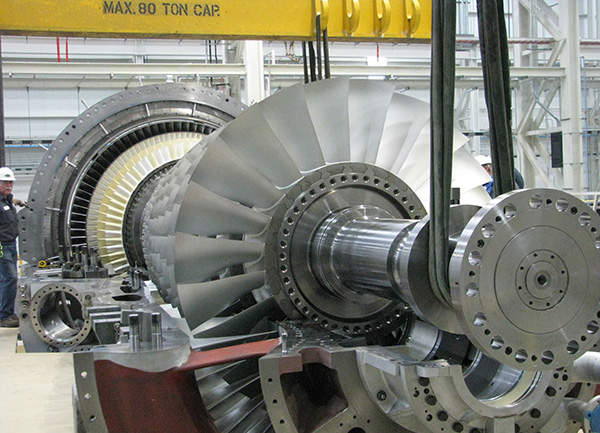
The Panda Temple power plant is fitted with equipment supplied by Siemens, including two SGT6-5000F gas turbines, one SST6-5000 steam turbine, two SGen6-1000A generators, one SGen6-2000H generator and the SPPA-T3000 instrumentation and control system.
The SGT6-5000F is a four-stage gas turbine with a power capacity of 208MW. The SST6-5000 steam engine, with a capacity up to 500MW, includes a combined high-pressure/intermediate-pressure cylinder and at least one double flow-low-pressure cylinder. The Shaping Power feature of the gas turbines enables the plant to generate higher yield during hotter days.
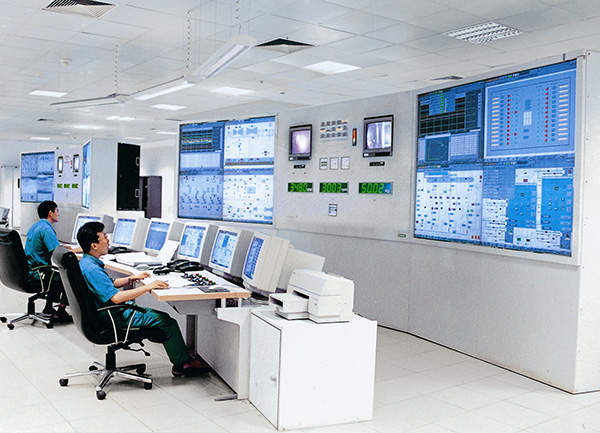
The SGen6-1000A is a hydrogen-cooled generator with up to 99% efficiency. Two Benson heavy duct-fired heat recovery steam generators will also be part of the plant equipment. The SPPA-T3000 (Siemens Power and Process Automation T3000) undertakes various power plant automation tasks, such as turbine control, boiler control and protection, balance of plant (BOP) and integration of third party systems.
The Panda plant is based on Siemens’ combined cycle Flex-Plant-30 technology. It provides the turbines with fast start capability. The plant can start generation within ten minutes from start-up, while full base-load power production can begin in less than an hour.
Finances and contractors for Texas’s power project
Related project
Buffalo Gap 2, Texas, United States of America
AES started commercial operation of the 233MW Buffalo Gap 2 wind farm expansion near Abilene, Texas, in August 2007.
When announced in 2007, the power plant project was estimated to cost roughly $750m. Panda Power Funds and other financial institutions funded the power plant with equity financing.
A long-term service agreement and order volume was purchased for approximately $300m by Panda Temple Power. Under the turnkey construction contract, Bechtel was responsible for the engineering, procurement, construction and commissioning of the facility.
Siemens supplied the power island equipment, including natural gas and steam turbines as well as waste heat recovery boilers. The company manufactured the turbines and generators at its production facility in Charlotte, North Carolina.
Under a subcontract with Siemens, NEM supplied two Benson heat recovery steam generators (HRSGs) for the power plant.
Environmental impact of the Panda Temple project
The plant was granted an air permit by the Texas Commission on Environmental Quality in October 2008.
The plant is claimed to one of the cleanest fossil-fueled plants in the country. Carbon monoxide (CO) emissions are less than ten parts per million (ppm), and nitrogen oxide (NOx) emissions are less than 2ppm.
Texan power market details
The power industry has been predicting a severe power crisis in Texas in the coming years. Power reserves were forecast to drop below 10% by 2014.
The state power grid operator, the Electric Reliability Council of Texas (ERCOT), announced in its 2010 annual report that the power reserves would fall from 21.8% to 12.3% in 2014 and further to 10.2% in 2015.
Stringent environmental rules are expected to result in the closure of older gas and coal-fired plants. Low wholesale power prices have also been discouraging the setting up of new plants in the state.
In 2012, state regulators decided to increase the wholesale price limit by 50% during power scarcity.
Related content
Silver Star 1 Wind Farm, Texas, United States of America
The Silver Star 1 wind farm added another 60MW to Texas’ increasing renewable power supply.