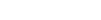

A new study from the Australian National University (ANU) has found that 22,000 sites across the country have potential for the development of fresh pumped hydro energy storage projects.
The sites could ensure a secure and cheap supply of clean electricity to Australia’s national grid and help create a zero-emissions grid, which is said will allow Australia to remove its dependence on coal and gas-fired power plants completely.

Discover B2B Marketing That Performs
Combine business intelligence and editorial excellence to reach engaged professionals across 36 leading media platforms.
The study claimed that the short-term, off-river pumped hydro energy storage (STORES) sites have a combined potential storage capacity of 67,000GWh, which is much more than the capacity needed for a zero-emissions grid.
Situated outside national parks and urban areas, each of the potential STORES sites could generate between 1GWh and 300GWh of energy. They require pairs of reservoirs at different altitudes in hilly terrain and can be joined by a pipe with a pump and turbine.
ANU Research School of Engineering professor Blakers said: “Australia needs only a tiny fraction of these sites for pumped hydro storage (about 450GWh) to support a 100% renewable electricity system.
“Fast tracking the development of a few of the best sites by 2022 could balance the grid when Liddell and other coal power stations close. Pumped hydro storage, including Snowy 2.0, can be developed fast enough to balance the grid with any quantity of variable wind and solar photovoltaic (PV) power generation, including 100% renewable energy.
US Tariffs are shifting - will you react or anticipate?
Don’t let policy changes catch you off guard. Stay proactive with real-time data and expert analysis.
By GlobalData“We found so many good potential sites that only the best 0.1% will be needed. We can afford to be choosy.”
Image: Potential short-term off-river pumped hydro energy storagesites in Australia. Photo: courtesy of ANU.