FRIENDSHIP SYSTEMS provides highly automated computational fluid dynamics (CFD) analysis software services for the design and shape optimisation of turbines and various components for power generation systems.
FRIENDSHIP SYSTEMS provides highly automated computational fluid dynamics (CFD) analysis software services for the design and shape optimisation of turbines and various components for power generation systems.
The company carries out CFD-driven design studies based on the CAESES software solution to obtain the best fluid-dynamic performance for their customers’ products.
Fully automated computational fluid dynamics (CFD) modelling
The flexible CAD modelling and flow simulation in CAESES are completely automated so that no manual interaction is required for comprehensive studies. This allows engineers to quickly investigate large sets of design candidates in powerful workstations and high-performance computing (HPC) clusters.
FRIENDSHIP SYSTEMS collaborates with all major CFD vendors and connects to open-source packages. These include FINE / Turbo, ANSYS CFX, STAR-CCM+, OpenFOAM, and any proprietary in-house tools.
The company’s CAESES software is used worldwide by leading companies in the energy and turbomachinery sector to improve the shape of complex flow-exposed components and create highly competitive, innovative products.
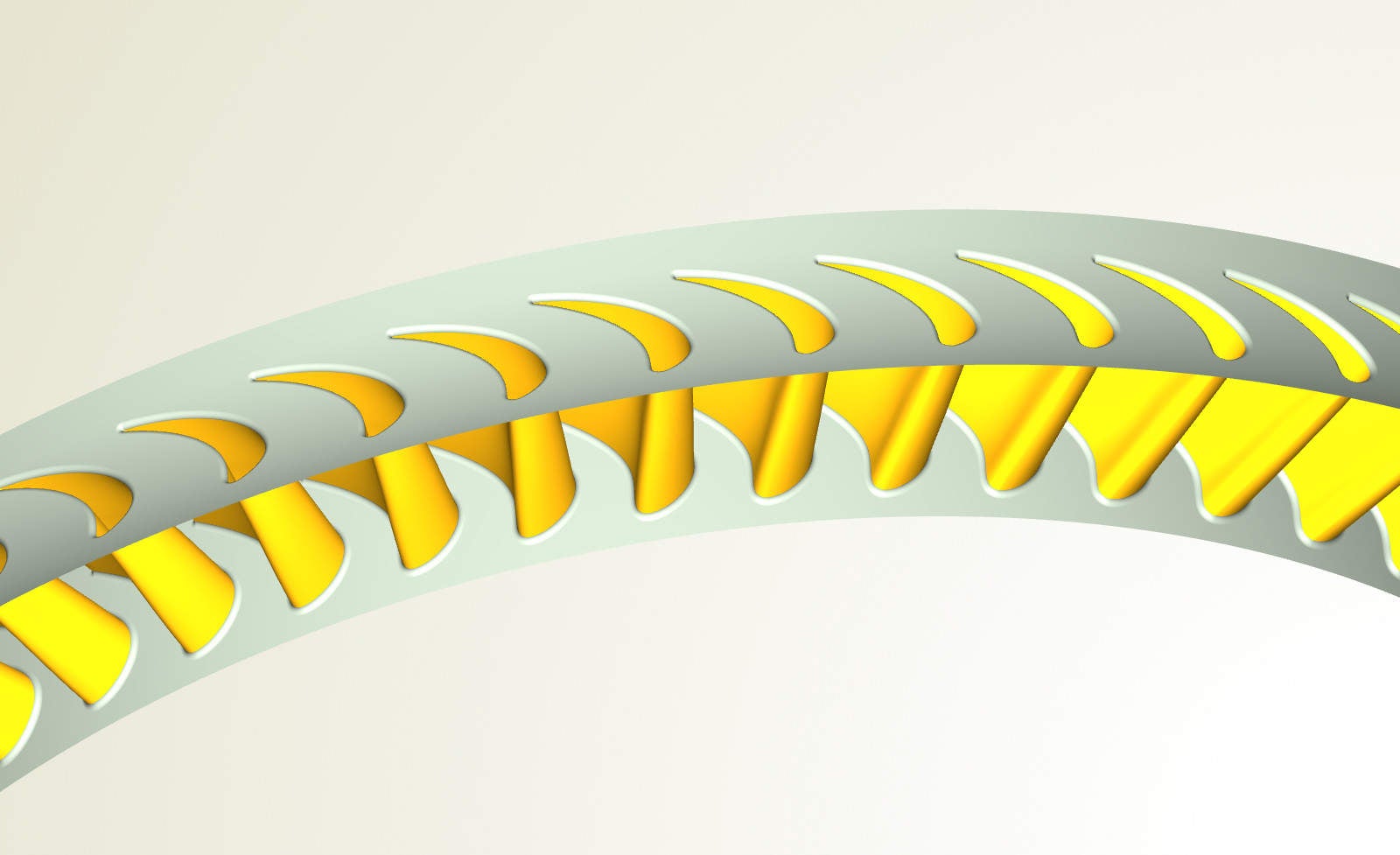
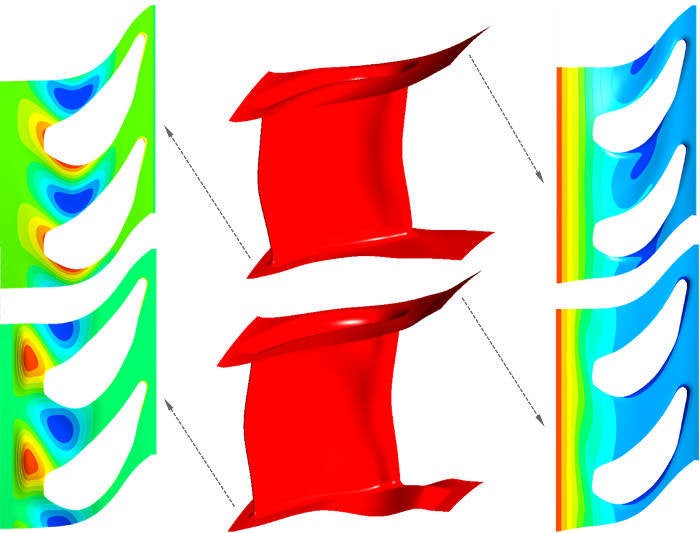
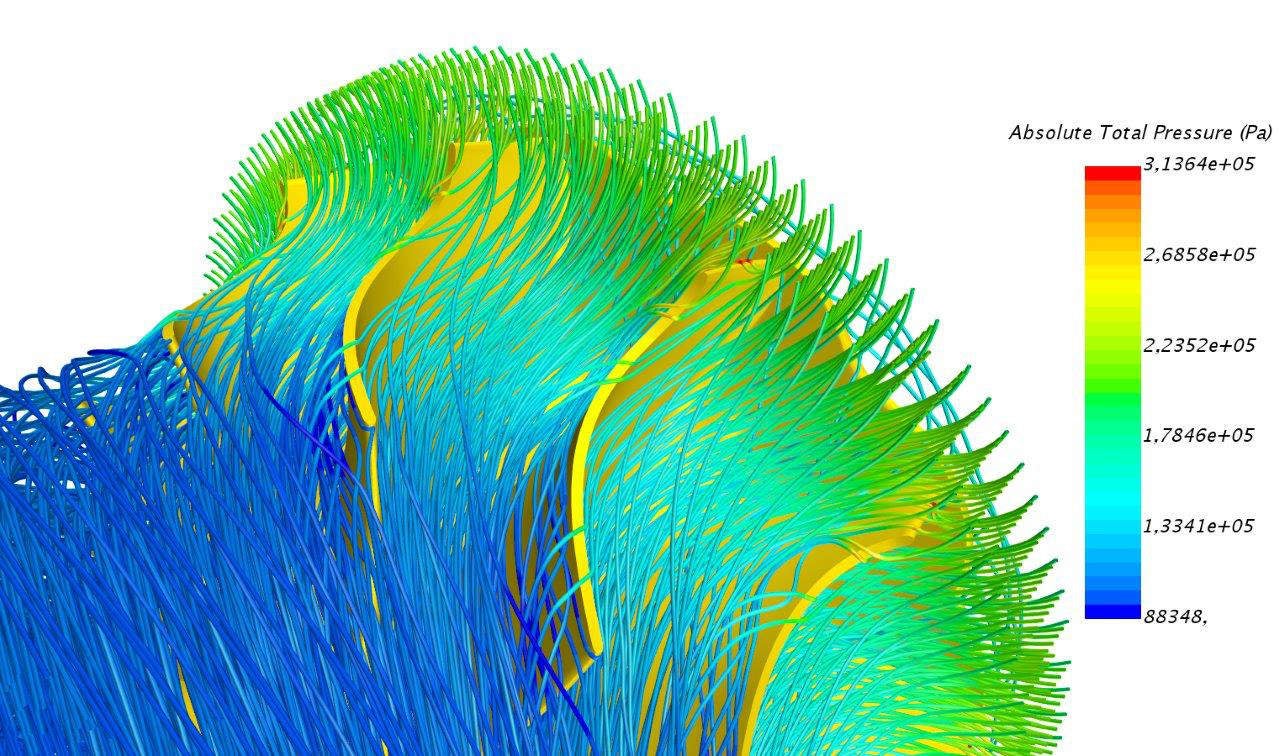
Turbine blades and endwall contouring
The shape details of turbine blades are essential to improve the efficiency of the entire power generation system. Optimising the blade shape can only be done in a fully automated process due to a large number of design configurations.
Endwall contouring is carried out to reduce secondary flow losses, while the number of design candidates largely increases due to the amount of flexibility in the modelling process.
CAESES allows engineers to fine-tune these details in a computerised way, using efficient geometry modelling techniques, CFD automation, and integrated state-of-the-art optimisation strategies.
The solution is not a black box turbine design tool. Instead, it allows engineers to build up completely customised workflows with robust blade geometries for shape optimisation tasks.
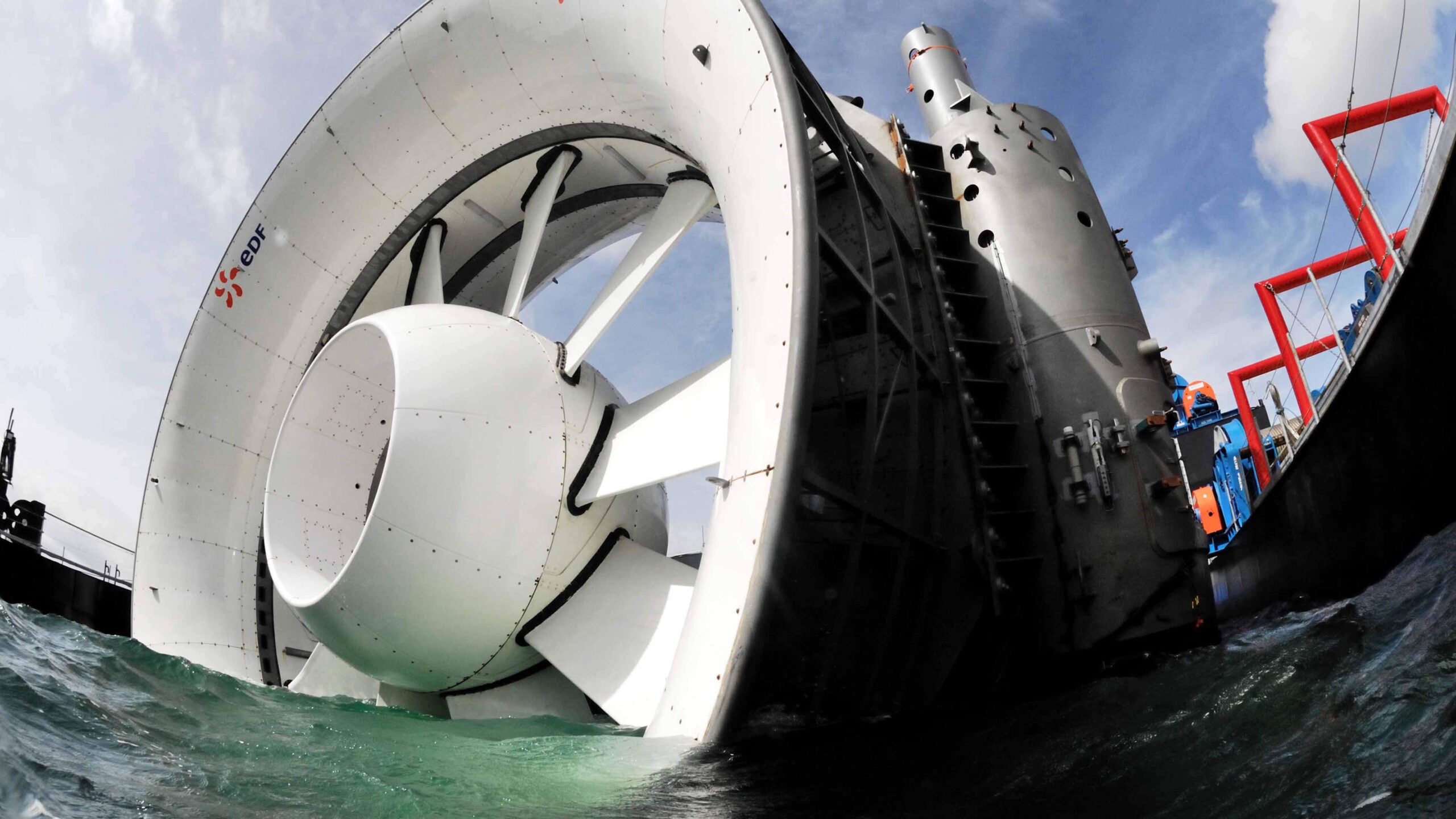
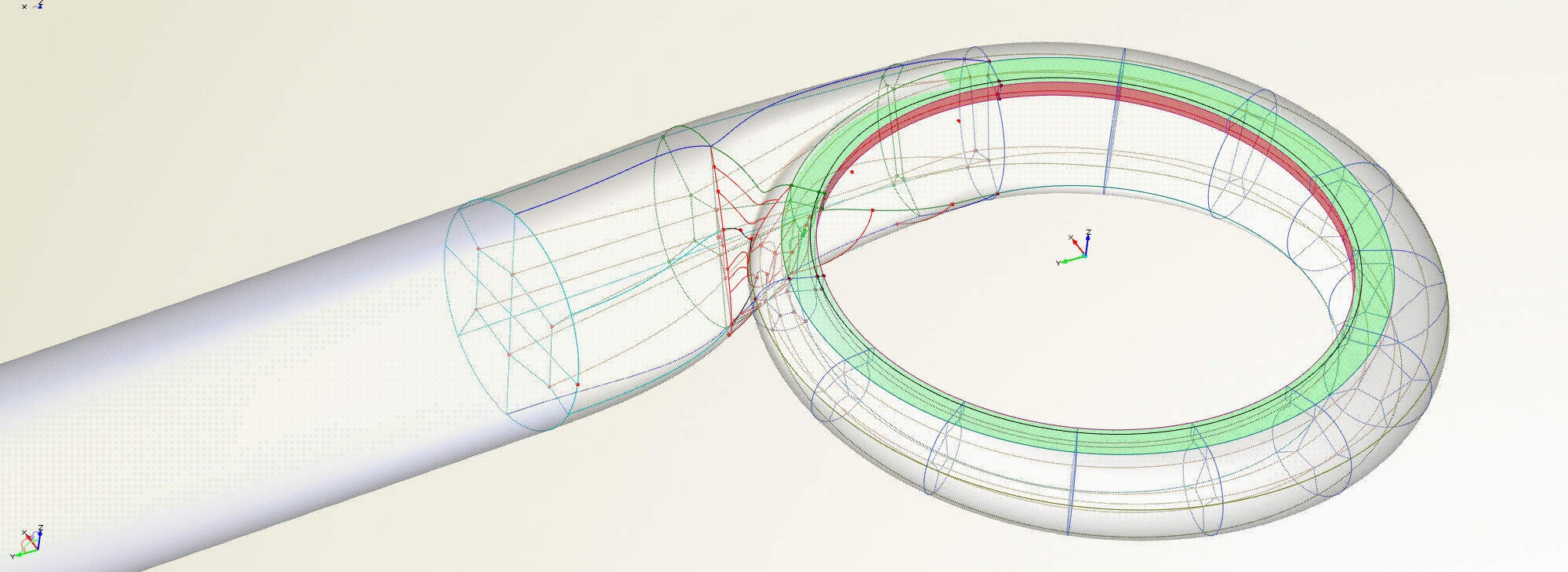
Hydroelectric turbines and tidal power systems
FRIENDSHIP SYSTEMS supports manufacturers of hydroelectric turbines and tidal power systems to design complex flow-exposed products. Due to the generalised blade design capabilities of CAESES, these turbines can also be modelled and investigated in larger studies using CFD.
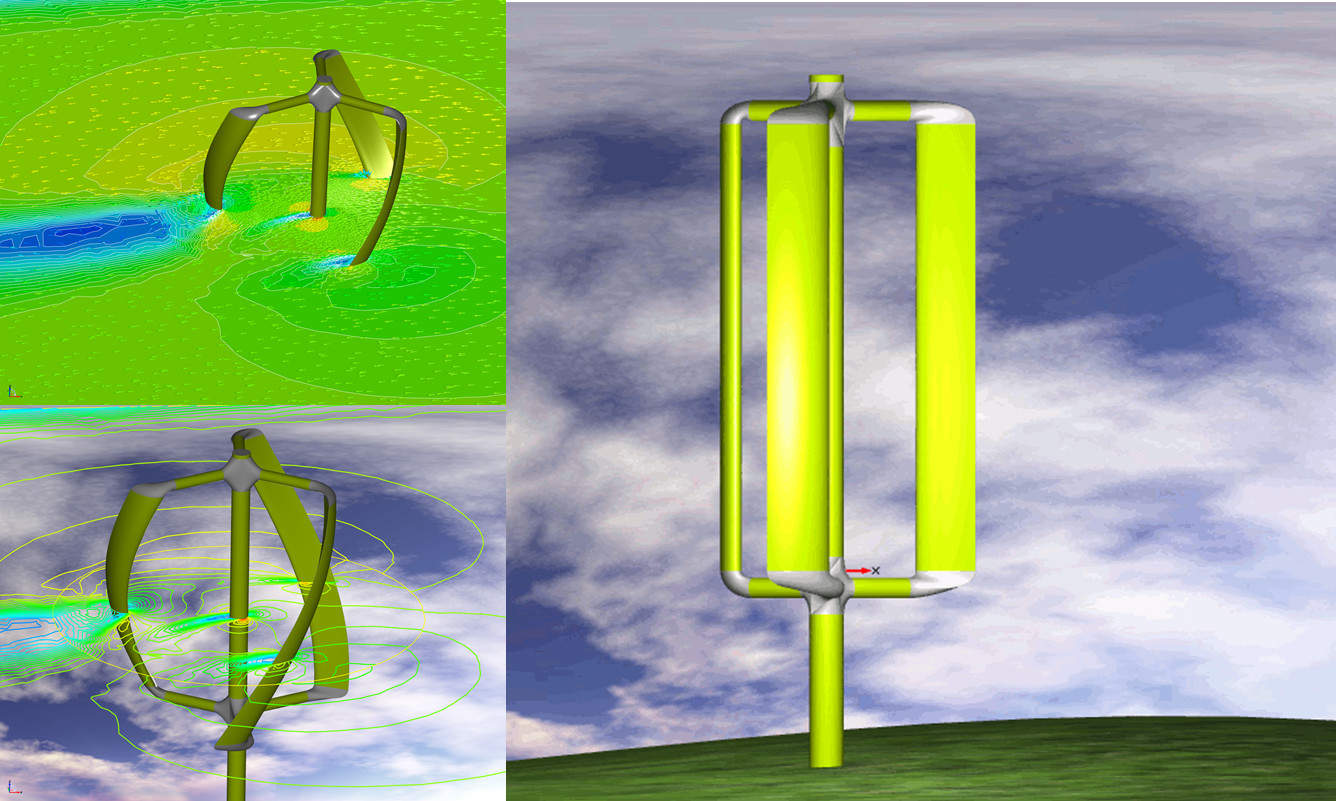
Design of wind turbines for the energy industry
CAESES provides specialised profile, surface and blade generation techniques that can be linked to the integrated optimisation strategies for the design of highly efficient wind turbines.
All required simulation tools can be coupled to the CAESES platform and other preliminary design tools. As a result, highly customised workflows are set up according to the client’s requirements and expertise.
Suzlon uses CAESES for the shape optimisation of wind turbines blades and is one of the leading suppliers in the renewable energy sector with more than 11,000 installations.
Shape optimisation of stationary engine components
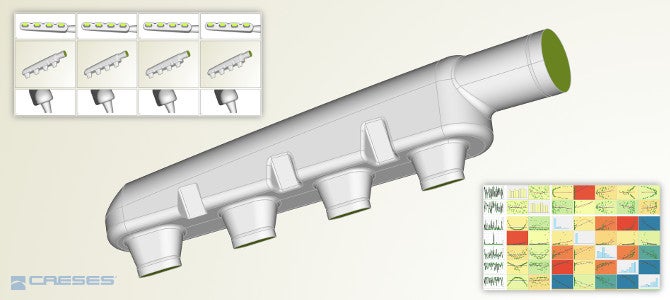
Liquid flow through various engine components needs to be optimised to minimise the pressure drop or to generate uniform fields. Example of engine components that are subject to optimisation include diffusers, pipes, intake and exhaust manifolds, piston bowls, as well as complete turbocharger systems.
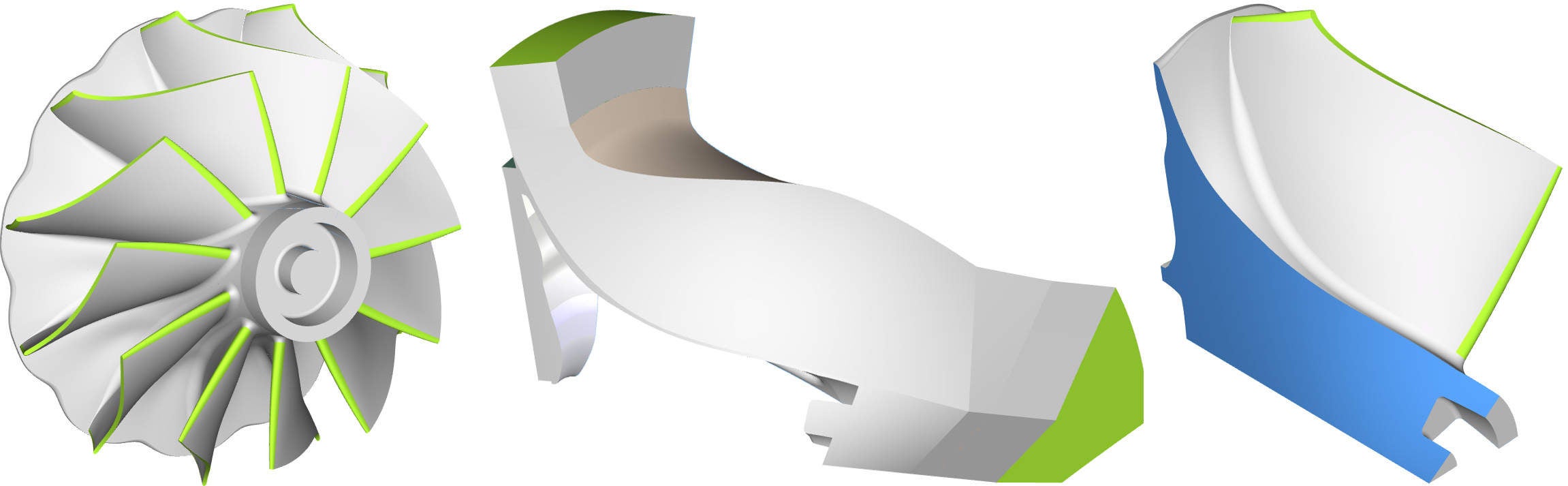
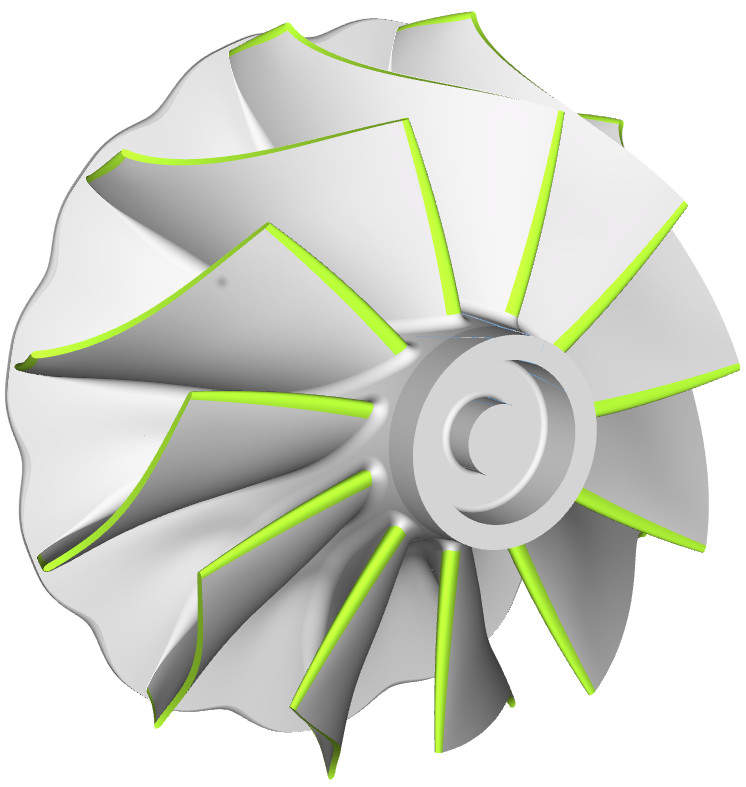
Flow-exposed parts of a turbocharger can be quickly developed with CAESES. The variable CAD models of the software give engineers the ability to create customised and optimal turbocharger components, including scallops, compressor impellers, and diffusers.
CFD and structural analysis are included in the optimisation loop, while only feasible designs are generated and analysed through simulation, largely increasing the speed of the overall turbocharger design process.
CAESES users typically create optimised turbocharger designs in a few days, instead of weeks or months.


 FRIENDSHIP SYSTEMS provides highly automated computational fluid dynamics (CFD) analysis software services for the design and shape optimisation of turbines and various components for power generation systems.
FRIENDSHIP SYSTEMS provides highly automated computational fluid dynamics (CFD) analysis software services for the design and shape optimisation of turbines and various components for power generation systems.