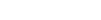GlobalData’s latest report, Smart Grid, is among the latest strategic intelligence reports from the industry analysis specialist. The report provides an industry analysis of the smart grid market, its growing demand and how it is disrupting power utilities and the power sector. The report focuses on trends related to the smart grid as a theme in technology, macroeconomic and regulatory trends. The report briefs on detailed analysis of the smart grid value chain.
The report is built as a single theme, offering in-depth research using data and information sourced from industry associations, company websites, government websites and statutory bodies. Information is also sourced through other secondary research sources, such as industry and trade magazines.
US Tariffs are shifting - will you react or anticipate?
Don’t let policy changes catch you off guard. Stay proactive with real-time data and expert analysis.
By GlobalDataGrowth in transmission infrastructure investment is accelerating to meet rising smart grid demand, with the power transmission market expected to expand strongly through the 2030s. This growth is being driven by government initiatives, renewable energy integration, the need for greater grid resilience and efficiency and the adoption of technologies such as smart meters, AI and the Internet of Things. The transmission investment is projected to increase from $372.6 billion in 2025 to $573.7 billion by 2030.
The transmission investment stood at $343.2 billion in 2024, increasing at a rate of 10.5% over 2023. Substations accounted for a significant part of the 2024 transmission investment at $246.4 billion, followed by the transmission lines at $96.4 billion. Transmission investment is estimated to grow at a compound annual growth rate of 9.2% between 2025 and 2030.

AI is improving smart grids by using real-time data and algorithms for demand forecasting, predictive maintenance and integrating renewables. It optimises power flow, balances supply and demand, automates responses to instabilities and prevents equipment failures — leading to fewer outages, less energy waste and a more reliable, sustainable grid. Companies such as Nvidia and Utilidata have partnered to make regional electrical grids smarter and more efficient by developing software-defined smart grid chips.
Utilities such as Duke Energy are leveraging AI and machine learning for operational aspects, including fleet management and predictive maintenance. Xcel Energy utilises the AI-powered Grid Vision software from eSmart Systems, which aids in visualising and analysing conditions of power lines and substations. E.ON has developed machine learning algorithms to predict the maintenance needs of medium voltage cables within its grid, aiming to reduce outages significantly. Southern Company is using AI through WeaveGrid, which supports the integration of electric vehicles (EVs) into the electric grid. This technology helps in optimising energy distribution and planning for EV infrastructure.
Data centres are playing a crucial role in the functioning and evolution of smart grids, primarily due to their significant energy demands and the integration of advanced technologies. They deliver essential data processing and storage functions to oversee energy distribution, incorporate renewable sources, enable AI-powered grid automation and contribute to grid services such as frequency regulation. Utilising technologies such as microgrids, energy storage systems and grid-interactive uninterruptible power supplies, data centres can refine their energy consumption, increase carbon consciousness, and proactively aid in creating a stable, resilient and sustainable power infrastructure. Data centres are pivotal in enhancing the reliability and efficiency of the electric grid. Initiatives such as the DCFlex programme, which involves collaboration between utilities and data centre technology companies, aim to integrate data centres with grid operations to support operational flexibility and improve grid integration. This has resulted in a notable surge in data centre projects, particularly driven by the increasing demand for data storage and processing capabilities, largely due to the rise of AI technologies.
It is imperative to note that advanced data centres can supply power back to the grid during emergencies – a feature known as bidirectional power flow. The smart grid market is projected to experience continued significant growth due to increasing demand for energy efficiency, renewable energy integration, the modernisation of energy infrastructure and supportive government policies. The deployment of technologies such as AI, big data and blockchain is leading toward enhanced grid management. Smart grid solutions will give utilities and large energy consumers the tools needed to transform how electricity is generated, delivered and consumed through advanced metering infrastructure and two-way communications for granular visibility.